Urban development is accelerating at an unprecedented pace, placing immense pressure on infrastructure, energy systems, and environmental sustainability. Among the most critical yet often overlooked components of modern cities is HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) technology. Recent HVAC innovations are reshaping how cities manage energy efficiency, indoor comfort, and environmental impact while supporting dense, mixed-use urban environments.
The Growing Role of HVAC in Modern Cities
As urban populations expand vertically and horizontally, HVAC systems are no longer just comfort tools. They have become strategic infrastructure assets that influence building performance, public health, and energy demand.
Key urban challenges HVAC systems now address include:
-
Rising energy consumption in dense building clusters
-
Urban heat island effects
-
Indoor air quality in high-occupancy spaces
-
Carbon reduction targets set by municipalities
Innovative HVAC solutions help cities meet these demands without compromising livability.
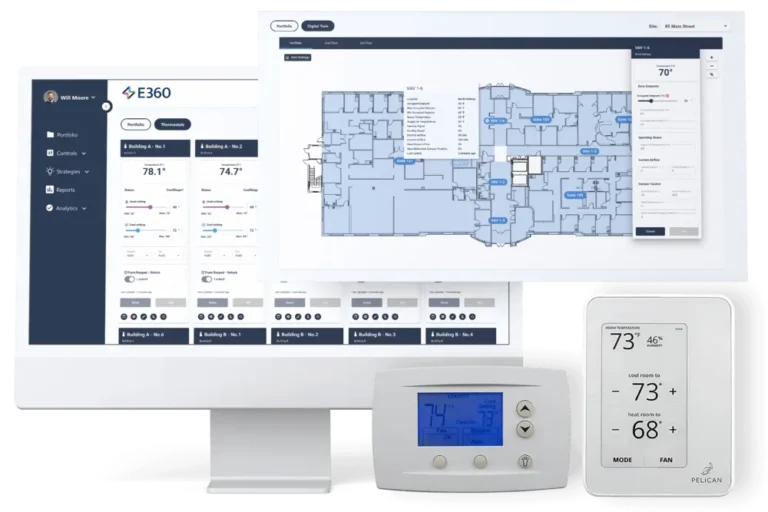
Smart HVAC Systems and Digital Integration
AI-Driven Climate Control
Modern HVAC systems increasingly rely on artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize performance. These systems analyze occupancy patterns, weather data, and energy pricing in real time.
Benefits include:
-
Reduced energy waste during low-occupancy periods
-
Predictive maintenance that prevents system failures
-
Improved comfort personalization for occupants
Integration with Smart City Platforms
HVAC technology is now interconnected with broader smart city ecosystems, allowing buildings to communicate with power grids and energy management platforms. This integration supports demand-response strategies that reduce strain during peak hours.
Energy-Efficient HVAC Solutions for Dense Urban Areas
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems
VRF systems are particularly suited for high-rise and mixed-use buildings common in urban centers. They provide simultaneous heating and cooling across different zones with minimal energy loss.
Key advantages
-
Precise temperature control per zone
-
Lower operating costs
-
Compact design ideal for space-constrained buildings
Heat Recovery and Reuse
Advanced HVAC systems can capture waste heat from one area of a building and redistribute it elsewhere. This innovation significantly improves overall energy efficiency in large urban structures.
District Heating and Cooling Networks
Centralized Urban Climate Control
District HVAC systems supply heating or cooling from a centralized plant to multiple buildings through underground networks. These systems are gaining traction in large cities focused on sustainability.
Urban benefits
-
Reduced equipment redundancy across buildings
-
Lower greenhouse gas emissions
-
Easier integration of renewable energy sources
District cooling is especially effective in business districts, airports, and mixed-use developments.
Sustainable and Low-Carbon HVAC Technologies
Electrification and Renewable Compatibility
The shift away from fossil fuels has accelerated the adoption of electric HVAC systems compatible with solar, wind, and geothermal energy. Heat pumps, in particular, play a central role in urban decarbonization strategies.
Low-GWP Refrigerants
Next-generation refrigerants with low global warming potential (GWP) are replacing traditional options. This change significantly reduces the environmental footprint of urban HVAC systems without sacrificing performance.
Indoor Air Quality as a Public Health Priority
Urban buildings face higher risks of airborne pollutants due to traffic emissions and high occupancy. HVAC innovations now prioritize advanced filtration and ventilation.
Notable advancements include:
-
HEPA and activated carbon filters
-
UV-C air purification technologies
-
Demand-controlled ventilation based on CO₂ levels
These systems contribute to healthier indoor environments in offices, residential towers, hospitals, and transit hubs.
Modular HVAC Design for Rapid Urban Expansion
Cities evolve quickly, and HVAC systems must adapt just as fast. Modular and scalable HVAC designs allow developers to expand or reconfigure buildings without replacing entire systems.
This flexibility supports:
-
Phased urban development projects
-
Mixed-use conversions
-
Reduced upfront infrastructure costs
The Future of HVAC in Urban Development
HVAC innovation will continue to align with urban priorities such as net-zero buildings, climate resilience, and occupant wellness. As regulations tighten and cities aim for smarter growth, HVAC systems will remain a cornerstone of sustainable urban planning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How do HVAC innovations reduce energy consumption in cities?
Advanced controls, heat recovery systems, and smart sensors optimize energy use by adjusting performance based on real-time demand.
2. Why are district cooling systems popular in urban areas?
They serve multiple buildings efficiently from a centralized source, reducing emissions, maintenance, and space requirements.
3. What role does HVAC play in smart city development?
HVAC systems integrate with digital infrastructure to support energy management, grid stability, and data-driven urban planning.
4. Are modern HVAC systems suitable for older urban buildings?
Yes, many innovations are designed for retrofitting, allowing legacy structures to improve efficiency without major reconstruction.
5. How does HVAC technology improve indoor air quality in cities?
Through advanced filtration, controlled ventilation, and air purification technologies that reduce pollutants and airborne pathogens.
6. What HVAC trends support climate goals in urban development?
Electrification, renewable energy integration, low-GWP refrigerants, and heat pump adoption are key contributors.
7. Can HVAC systems help cities adapt to climate change?
Yes, resilient HVAC designs enhance thermal comfort during extreme weather while reducing strain on urban energy systems.